Adapted from http://www.umich.edu/~marcons/Crusades/timeline/detailedtimeline.html
| Date(s) | Event |
|---|---|
| 1040 – 1055 | Turks migrate from central Asia to southwest Asia, conquer Persia, and invade Armenia and Iraq, finally capturing Baghdad, the Abbasid capital city |
| 1067 – 1070 | Turks invade Byzantine territory in Asia Minor (today’s Turkey); Turkic forces take Jerusalem from the Fatimid dynasty of North Africa |
| 1071 | Turkic forces defeat Byzantine forces at the Battle of Manzikert and found the Sultanate of Rum in Asia Minor |
| 1054 | Schism (split) of the Christian Church into the Roman Catholic centered in the Papacy in Rome, and Greek Orthodox centered in the Byzantine capital of Constantinople |
| 1061 – 1091 | Christian forces under the Normans invade and defeat Muslim ruled Sicily, but retain Muslim cultural influence under Norman rule. |
| 1085 | Antioch in northern Syria conquered by Turks; in Spain, the Muslim city of Toledo is captured by Christian forces under Alfonso VI |
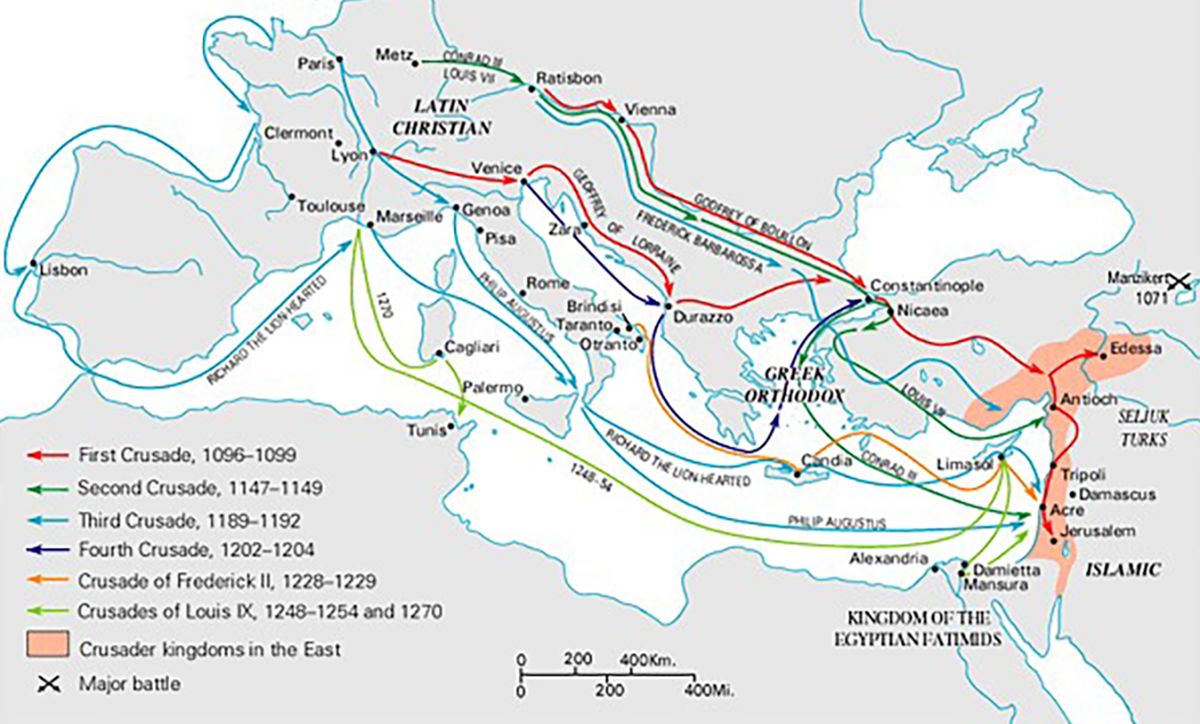
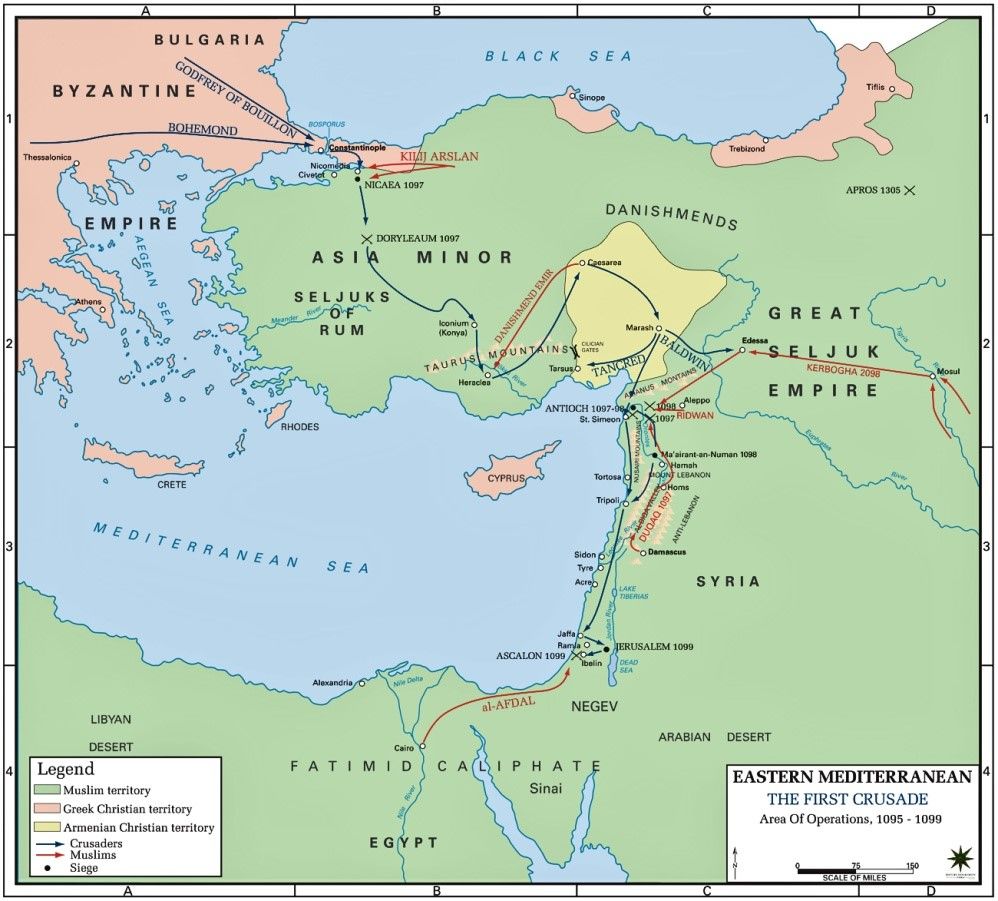
| 1096 | Start of the First Crusade |
| March 1095 | Byzantine Empire requests Pope Urban II's help against Turkic warrior tribes who have migrated into Asia Minor |
| November 27, 1095 | Pope Urban II preaches the First Crusade |
| 1096 | Fatimids retake Jerusalem from Seljuk Turks |
| Spring, Summer 1096 | Crusaders massacre Jews in Europe |
| Spring 1096 | People's Crusade leaves for Holy Land but most end the march near Hungary by August 1096 |
| August 15, 1096 | Official beginning of First Crusade set by Pope Urban II |
| October 6, 1096 | Crusader armies under Peter and Walter destroyed at Nicaea by Kilij Arslan |
| Fall 1096 | Crusaders of official First Crusade reach Constantinople; Alexius I Comnenus accepts their oaths of loyalty and pledges to return lands under Byzantine control |
| April 1097 | Crusaders cross the Bosporus into Asia |
| Early June 1097 | Crusaders arrive at Nicaea while Kilij Arslan is away fighting his opponent Danishmend |
| June 19, 1097 | Nicaea surrenders to Byzantine forces |
| June 26–28, 1097 | Crusaders invade Asia Minor |
| July 1, 1097 | Turks under Kilij Arslan fail to defeat Crusaders at Dorlyaeum |
| October 21, 1097 | Crusaders reach Antioch, ruled by Turkic leader Yaghi-Suyan |
| Early February 1098 | Muslim relief force under the Turkish leadership moves toward Antioch |
| February 6, 1098 | Baldwin reaches Edessa (al-Ruha in Arabic) |
| March 9, 1098 | Edessa's ruler is killed in a riot |
| March 10, 1098 | Edessa established as the first Latin settlement in the East under Crusade leader Baldwin after its Turkic leader flees |
| June 5, 1098 | Muslim army relief force arrives and besieges Crusaders in Antioch |
| Mid-November 1098 | Armies of Raymond of St. Gilles and Robert of Flanders arrive at Ma'arat en Nu'man, spurred on by ordinary soldiers |
| December 11-2, 1098 | Ma'arat en Nu'man falls to the Crusaders |
| January/March 1099 | Crusader armies force their leader Raymond to continue to Jerusalem |
| February/May 1099 | Crusaders besiege 'Arqah but abandon siege and go on to Jerusalem |
| June 6, 1099 | Crusader leader Tancred seizes Bethlehem |
| June 7, 1099 | Main body of Crusaders arrives at Jerusalem |
| July 15, 1099 | Crusaders seize and sack the city of Jerusalem and massacre Muslims, Eastern Christians, and Jews; Godfrey elected ruler of the city |
| July 19–22, 1099 | Pope Urban II dies, never hearing news of capture of Jerusalem |
| August 11–12, 1099 | Crusaders defeat Egyptian army at Ashdod |
| 1099 | Al-Harawi of Damascus leads group of refugees to Baghdad to plead for help (see poem) |
| 1100 | Baldwin chosen first Crusader king of Jerusalem |
| Summer 1100 | Turkic leader Danishmend captures Crusader leader Bohemund |
| November 15, 1100 | Pope Paschal II preaches new crusade, threatening excommunication for failure to fulfill their vows |
| 1101 | New wave of Crusaders defeated in Asia Minor |
| 1104 | Crusader leader Baldwin takes port city of Acre |
| 1104 | Muslims defeat Franks at Harran, preventing them from moving further east into Muslim territory |
| 1109 | Tripoli falls to the Crusader armies after a brutal siege of 2000 days |
| 1110 | Crusaders seize cities of Beirut and Saida |
| 1111 | Aleppo's chief judge Ibn al-Khashab organizes riot in Baghdad to force the government to send military help against the Franks |
| 1112 | Muslim forces keep Franks from seizing Tyre |
| 1113 | Hospitallers, knightly Order of St. John is founded as Crusader force |
| Spring 1115 | Alliance of Muslims and Franks in Syria fight Seljuk Sultan Muhammad ibn Malikshah |
| 1119 | Ilghazi of Aleppo defeats Franks at Sarmada |
| 1120 | Order of the Knights Templar is founded as Crusader force |
| July 1124 | Franks seize Tyre, giving them entire coastline up to Ascalon |
| 1125 | Beirut peasants revolt |
| 1127 | Zangi becomes the ruler of Mosul and leader of resistance to the Franks |
| 1128 | Franks fail to seize Damascus |
| 1128 | Zangi takes the city of Aleppo |
| 1135 | Zangi fails to take Damascus |
| 1137 | Zangi captures King Fulk of Jerusalem but releases him |
| 1139 | Zangi unsuccessfully besieges Damascus |
| 1144 | Zangi seizes Edessa, defeating the first crusader state |
| 1146 | Zangi dies, and his son Nur al-Din inherits Aleppo |
| 1147-1149 | The Second Crusade begins, which includes Crusades in parts of Muslim-ruled Spain, Eastern Germany and the East (Outremer in French) |
| 1147 | Spanish Crusaders take Lisbon from Muslim rule |
| 1148 | Crusader armies under Conrad of Germany and Louis VII of France besiege Damascus, but are turned back by Nur al-Din's forces |
| 1154 | Nur al-Din takes Damascus, unifying Muslim territories in Syria |
| 1163 – 1169 | Nur al-Din's general Shirkuh fights to deliver Egypt to Nur al-Din |
| 1169 | Shirkuh rules Egypt as vizier, but soon dies; Saladin, his nephew, becomes ruler of Egypt |
| 1170 | Nur al-Din's brother dies, giving him control of Mosul |
| 1171 | Saladin ends Fatimid rule in Egypt and establishes Ayyubid dynasty; Competition between Nur al-Din and Saladin ensues |
| 1174 | Nur al-Din dies; Saladin seizes control of Damascus |
| 1183 – 1185 | Saladin takes control of Aleppo, uniting Egypt and Syria under his rule, then takes control of Mosul |
| 1185 | Saladin officially controls Egypt and Damascus, Aleppo and Mosul |
| July 4, 1187 | Saladin defeats Frankish Crusaders at the Battle of Hattin |
| October 2, 1187 | Saladin retakes Jerusalem and lands under Frankish control; Franks retain only cities of Tyre, Tripoli, and Antioch |
| 1189 – 1192 | Third Crusade brings famous Crusader leaders Richard I of England, Philip II of France, and Holy Roman Emperor Frederick I |
| June 1190 | Frederick I dies en route to the Holy Land |
| Summer 1191 | Kings Richard and Philip take the city of Acre and name Jerusalem's ruler; Philip leaves for home, while Richard takes Arsuf and Jaffa and fortifies Ascalon |
| September 2, 1192 | Richard and Saladin end their fighting with a treaty, and Richard leaves for home in England |
| 1193 | Saladin dies, and after his succession is contested, Saladin's brother al-Adil rules. |
| Spring 1197 | Frederick I's son Henry VI departs to join the Crusade, but dies in the same year. |
| July 1, 1198 | Henry VI's supporters negotiate a treaty with Muslim rulers and return home |
| 1198 | Crusader Order of Teutonic Knights is founded with Acre as its base. |
| 1202 – 1204 | Fourth Crusade begins |
| July 17, 1203 | Crusaders invade and sack Byzantine capital of Constantinople, naming Alexius IV as ruler |
| April 12, 1204 | Crusaders take Constantinople and make Byzantine lands into a Latin Empire |
| 1209-1229 | Albigensian Crusade turns against heretics at home in southern France |
| 1212 | Children's Crusade begins and ends in tragedy |
| 1213 – 1216 | Pope Innocent III begins planning the Fifth Crusade; he dies, and Pope Honorius III continues his plan |
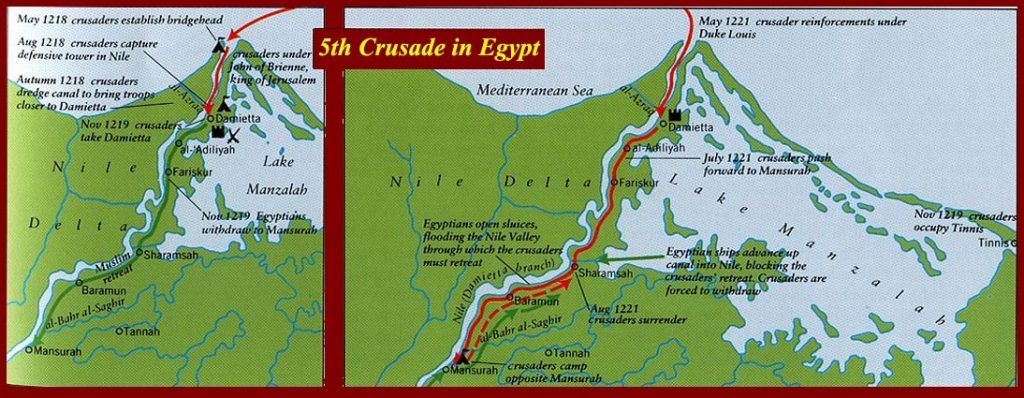
| 1217 – 1221 | Fifth Crusade begins; Invasion of Egypt under the rule of al-Malik al-Kamil is led by Cardinal Pelagius; Crusaders besiege Damietta and try to Crusaders try take Cairo; Al-Kamil's forces and rising Nile isolates and defeats Crusader army; Al-Kamil provides bread and supplies to save Crusader army from starvation |
| 1219 | Sultan al-Kamil receives Francis of Assisi at his court for interreligious discussion and allows Francis to preach; Francis's stay at court influences his views of Islam and faith practice |
| 1228 – 1229 | Holy Roman Emperor Frederick II crusades in Egypt without papal support; al-Kamil negotiates treaty with Frederick II over control of Jerusalem. |
| 1235 | Byzantines retake Asia Minor |
| 1236 – 1238 | In Spain, Ferdinand III of Castile attacks the city of Cordova, the Christian army of Aragon takes the city of Valencia from Muslim rule |
| 1244 | Franks lose Jerusalem for the final time |
| 1245 | Pope Innocent IV sends missionaries to Mongols to attempt alliance against Muslims in Asia and Near East |
| 1247 | Louis IX plans a Crusade, but contact with Frederick divulges his plans to al-Kamil's son, Ayyub |
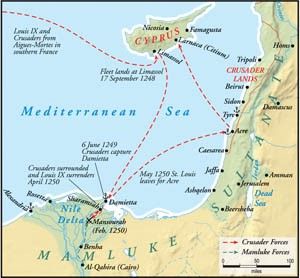
| 1248 – 1254 | Sixth Crusade |
| 1248-1250 | Louis IX of France invades Egypt; he seizes Damietta, but is defeated and captured at the city of Mansurah; released for ransom and return of Damietta |
| 1248 – 1250 | Ayyubid dynasty in Egypt ends, Mamluk rule begins |
| February 1258 | Mongols under Genghis Khan's grandson Hülegü invade and destroy Baghdad, massacre inhabitants and kill the last 'Abbasid caliph |
| January 1260 | Mongols under Hülegü take Aleppo and Damascus; Mongol ruler dies and Hulegu returns to Asia, relieving invasion threat to Europe |
| September 3, 1260 | Mamluk armies defeat Mongols at the Battle of 'Ayn Jalut (Goliath Spring), and take city of Damascus; Baybars becomes ruler of Egypt |
| July 25, 1261 | Byzantines recapture Constantinople, ending the Latin Empire in the East |
| May 18, 1268 | Baybars seizes Antioch and Jaffa |
| 1270 | Seventh Crusade begins with Louis IX forces attacking Tunis; death of Louis IX |
| April 26 or 27, 1289 | Mamluk sultans Qalawun and son Khalil retake Tripoli and Acre from Franks |
| 1291 | Effective end of the Great Crusades; remaining Crusaders retreat to the island of Cyprus |
Map Sources: “MedEurope Tutorial 2: Map of Medieval Europe.” MedEurope Tutorial 2 (blog). http://medeuropetut2.blogspot.com/p/map-of-medieval-europe.html; “Map of the First Crusade 1095-1099.” http://www.emersonkent.com/map_archive/first_crusade.htm; “The Battle of Al Mansourah and the Seventh Crusade, 1251.” http://warfarehistorynetwork.com/daily/military-history/the-battle-of-al-mansourah-and-the-seventh-crusade-1251-2/; “http://Www.Mmdtkw.Org/CRUS-Unit8Images.Html.” http://www.mmdtkw.org/CRUS-Unit8Images.html.
